As Illumina sequencings are becoming more and more popular, there are various sequencing centers available for sequencing services around the nation. Here at UT-Austin, we have a renowned sequencing center (UT-Austin GSAF) that has been greatly helpful to my own work. However, recently we have had good experience with MD Anderson Science Park Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) Facility. So in this post, I am going to compare the sequencing prices between these two centers for future reference.
Since the two sequencing centers have their sequencing prices posted online, I will do some web scraping to collect the data, and data cleaning for visualizing the comparisons.
%matplotlib inline
import urllib.request
import pandas as pd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sequencing_tools.viz_tools import okabeito_palette
For MD Anderson Science park price, I will download the data from their website.
mda = 'https://www.mdanderson.org/research/research-resources/core-facilities/next-generation-sequencing-core/services.html'
mda_html = urllib.request.urlopen(mda)
soup = BeautifulSoup(mda_html, 'lxml')
tabs = soup.find_all('table')
table = tabs[-1]
mda_df = pd.read_html(str(table),
flavor='bs4',
header=0,
index_col = 0)[0]
mda_df
| NGS User Group Member Price (per lane) | MDACC Faculty, UT System, BCM w/ MOU Price (per lane) | *External Out-of-Network Price (per lane) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Service | |||
| HiSeq 3000 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 50 bp, single read | $966.41 | $1,100.71 | $2,177.47 |
| 75 bp, paired end | $1,746.41 | $1,880.71 | $3,425.47 |
| 100 bp, paired end | $2,089.61 | $2,223.91 | $3,974.59 |
| 150 bp, paired end | $2,431.25 | $2,565.55 | $4,521.22 |
| NextSeq 500 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| High Output: | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 75 bp, single read | $1,632.95 | $1,853.96 | $3,238.11 |
| 75 bp, paired end | $3,085.83 | $3,306.84 | $5,562.72 |
| 150 bp, paired end | $4,904.79 | $5,125.80 | $8,473.06 |
| Mid Output: | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 75 bp, paired end | $1,232.55 | $1,453.56 | $2,597.47 |
| 150 bp, paired end | $1,941.83 | $2,162.84 | $3,732.32 |
| MiSeq | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 50 bp, single read (v2 chemistry) | $948.99 | $1,132.53 | $1,358.78 |
| 150 bp, paired end (v2 chemistry) | $1,202.19 | $1,481.73 | $1,707.98 |
| 300 bp, single read (v2 chemistry) | $1,202.19 | $1,481.73 | $1,707.98 |
| 300 bp, paired end (v3 chemistry) | $1,782.99 | $2,177.73 | $2,403.98 |
Now, I need to clean up the table to make it more easily to manipulate. I will need a function to assign the platform (sequencing machines) for each run type (X bp, paired|single end). Then, I will only look at the member price, since that’s what we pay for.
def clean_mda_index(idx, data_col):
platform = ''
clear = False
new_idx = []
for i, dc in zip(idx,data_col):
if pd.isnull(dc):
if clear:
platform = ''
clear=False
platform = platform + i + '_'
new_idx.append(platform)
else:
new_idx.append(platform + i)
clear = True
return new_idx
mda_price_df = mda_df \
.assign(seq_type = lambda d: clean_mda_index(d.index, d.iloc[:,0])) \
.assign(seq_type = lambda d: np.where(d.seq_type.str.contains('Mid Output'),
'NextSeq 500_' + d.seq_type,
d.seq_type))\
.reset_index() \
.drop('Service', axis=1) \
.pipe(lambda d: d[~pd.isnull(d.iloc[:,1])]) \
.assign(platform = lambda d: d.seq_type.str.split('_', expand=True).iloc[:,0]) \
.assign(basepair = lambda d: d.seq_type.str.extract('_([0-9]+)', expand=False).astype(int)) \
.assign(ends = lambda d: d.seq_type.str.extract('(single|paired)', expand=False)) \
.pipe(lambda d: d[~d.seq_type.str.contains('Mid')]) \
.assign(md_price = lambda d: d.iloc[:,0].str.replace('[,$]','').astype(float))\
.assign(machine = lambda d: d.platform.str.replace(' [0-9]+','')) \
.assign(total_base = lambda d: np.where(d.ends == "paired", d.basepair * 2, d.basepair))\
.assign(ends = lambda d: np.where(d.machine=="MiSeq", 'single', d.ends))\
.filter(regex = 'platform|total|ends|md_price|machine') \
.drop_duplicates()
mda_price_df
| platform | ends | md_price | machine | total_base | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HiSeq 3000 | single | 966.41 | HiSeq | 50 |
| 2 | HiSeq 3000 | paired | 1746.41 | HiSeq | 150 |
| 3 | HiSeq 3000 | paired | 2089.61 | HiSeq | 200 |
| 4 | HiSeq 3000 | paired | 2431.25 | HiSeq | 300 |
| 7 | NextSeq 500 | single | 1632.95 | NextSeq | 75 |
| 8 | NextSeq 500 | paired | 3085.83 | NextSeq | 150 |
| 9 | NextSeq 500 | paired | 4904.79 | NextSeq | 300 |
| 14 | MiSeq | single | 948.99 | MiSeq | 50 |
| 15 | MiSeq | single | 1202.19 | MiSeq | 300 |
| 17 | MiSeq | single | 1782.99 | MiSeq | 600 |
For UT GSAF price, we will download the table from UT GSAF website.
gsaf = 'https://wikis.utexas.edu/display/GSAF/Library+Prep+and+NGS+Pricing+Descriptions'
gsaf_html = urllib.request.urlopen(gsaf)
soup = BeautifulSoup(gsaf_html, 'lxml')
tabs = soup.find_all('table')
gsaf_df = pd.read_html(tabs[0].prettify(),
flavor='bs4',
index_col = None,
header=0)[0]
gsaf_df
| Platform | Run Type | Internal / UT | External Academic | External Commercial | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | HiSeq 2500 | SR 50 | $1052 | $1331 | $1357 |
| 1 | HiSeq 2500 | SR 100 | $1428 | $1806 | $1842 |
| 2 | HiSeq 2500 | PE 125 | $2520 | $3187 | $3250 |
| 3 | HiSeq 4000 | SR 50 (1) | $ 1,043 | $ 1,319 | $1,345 |
| 4 | HiSeq 4000 | PE 150 (1) | $ 2,562 | $ 3,239 | $ 3,266 |
| 5 | HiSeq 4000 | SR 50 | $ 1,697 | $ 2,146 | $ 2,173 |
| 6 | HiSeq 4000 | PE 75 | $ 14,494 | $ 18,327 | $ 18,531 |
| 7 | NextSeq 500 | SR 75 H.O (1,3) | $ 2,302 | $ 2,906 | $ 3,060 |
| 8 | NextSeq 500 | PE 75 H.O . (1,3) | $ 3,826 | $ 4,834 | $ 4,988 |
| 9 | NextSeq 500 | PE 150 H.O. | $ 5,735 | $ 7,250 | $ 7,404 |
| 10 | MiSeq | V2 - 300 cycles | $ 1,627 | $ 2,054 | $ 2,157 |
| 11 | MiSeq | V2 - 500 cycles (1) | $ 1,771 | $ 2,236 | $ 2,339 |
| 12 | MiSeq | V3 - 150 cycles | $ 1,463 | $ 1,847 | $ 1,950 |
| 13 | MiSeq | V3 - 600 cycles (1) | $ 2,183 | $ 2,758 | $ 2,860 |
The resulting table is much more easier to be interpreted, since it is in a clean format. Again, I will only look at the Internal prices.
gsaf_price_df = gsaf_df\
.iloc[:, :3] \
.assign(machine = lambda d: d.Platform.str.replace(' [0-9]+','')) \
.assign(basepair = lambda d: d['Run Type'].str.extract(' ([0-9]+)', expand=False).astype(int)) \
.assign(ends = lambda d: np.where(d['Run Type'].str.contains('PE'), 'paired', 'single')) \
.assign(total_base = lambda d: np.where(d.ends == "paired",
d.basepair * 2,
d.basepair))\
.assign(gsaf_price = lambda d: d['Internal / UT'].str.replace('[$.,]','').astype(float)) \
.filter(regex = 'total|price|machine|ends|Platform')
gsaf_price_df
| Platform | machine | ends | total_base | gsaf_price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | HiSeq 2500 | HiSeq | single | 50 | 1052.0 |
| 1 | HiSeq 2500 | HiSeq | single | 100 | 1428.0 |
| 2 | HiSeq 2500 | HiSeq | paired | 250 | 2520.0 |
| 3 | HiSeq 4000 | HiSeq | single | 50 | 1043.0 |
| 4 | HiSeq 4000 | HiSeq | paired | 300 | 2562.0 |
| 5 | HiSeq 4000 | HiSeq | single | 50 | 1697.0 |
| 6 | HiSeq 4000 | HiSeq | paired | 150 | 14494.0 |
| 7 | NextSeq 500 | NextSeq | single | 75 | 2302.0 |
| 8 | NextSeq 500 | NextSeq | paired | 150 | 3826.0 |
| 9 | NextSeq 500 | NextSeq | paired | 300 | 5735.0 |
| 10 | MiSeq | MiSeq | single | 300 | 1627.0 |
| 11 | MiSeq | MiSeq | single | 500 | 1771.0 |
| 12 | MiSeq | MiSeq | single | 150 | 1463.0 |
| 13 | MiSeq | MiSeq | single | 600 | 2183.0 |
I notice there’s a duplicated price of HiSeq 4000 single end 50-nt (1043 USD vs 1697.0 USD), so I will take the lowest one, and merge with the science park prices.
merge_df = gsaf_price_df\
.groupby(['Platform','machine','ends','total_base'], as_index=False)\
.agg({'gsaf_price':np.min})\
.merge(mda_price_df, how ='outer')
merge_df
| Platform | machine | ends | total_base | gsaf_price | platform | md_price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | HiSeq 2500 | HiSeq | paired | 250 | 2520.0 | NaN | NaN |
| 1 | HiSeq 2500 | HiSeq | single | 50 | 1052.0 | HiSeq 3000 | 966.41 |
| 2 | HiSeq 4000 | HiSeq | single | 50 | 1043.0 | HiSeq 3000 | 966.41 |
| 3 | HiSeq 2500 | HiSeq | single | 100 | 1428.0 | NaN | NaN |
| 4 | HiSeq 4000 | HiSeq | paired | 150 | 14494.0 | HiSeq 3000 | 1746.41 |
| 5 | HiSeq 4000 | HiSeq | paired | 300 | 2562.0 | HiSeq 3000 | 2431.25 |
| 6 | MiSeq | MiSeq | single | 150 | 1463.0 | NaN | NaN |
| 7 | MiSeq | MiSeq | single | 300 | 1627.0 | MiSeq | 1202.19 |
| 8 | MiSeq | MiSeq | single | 500 | 1771.0 | NaN | NaN |
| 9 | MiSeq | MiSeq | single | 600 | 2183.0 | MiSeq | 1782.99 |
| 10 | NextSeq 500 | NextSeq | paired | 150 | 3826.0 | NextSeq 500 | 3085.83 |
| 11 | NextSeq 500 | NextSeq | paired | 300 | 5735.0 | NextSeq 500 | 4904.79 |
| 12 | NextSeq 500 | NextSeq | single | 75 | 2302.0 | NextSeq 500 | 1632.95 |
| 13 | NaN | HiSeq | paired | 200 | NaN | HiSeq 3000 | 2089.61 |
| 14 | NaN | MiSeq | single | 50 | NaN | MiSeq | 948.99 |
Let’s see if prices from both centers are correlated.
plt.rc('xtick', labelsize=15)
plt.rc('ytick', labelsize=15)
plt.rc('axes',labelsize=15)
p = sns.FacetGrid(data = merge_df,
hue = 'machine',
size = 5)
p.map(plt.scatter, 'md_price','gsaf_price')
p.add_legend(title = '')
p.set(xlabel = 'MD Anderson Science park\nsequencing cost (USD)',
ylabel = 'UT-Austin GSAF\nsequencing cost (USD)')
# label outlier
for i, row in merge_df.iterrows():
if row['gsaf_price'] > 10000:
label = row['machine'] + ' ' + str(row['total_base']) + ' bp'
p.fig.axes[0].text(row['md_price'] + 200,
row['gsaf_price'],
label)
p.fig.axes[0].plot(range(5000), color = 'black')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x11cd434a8>]
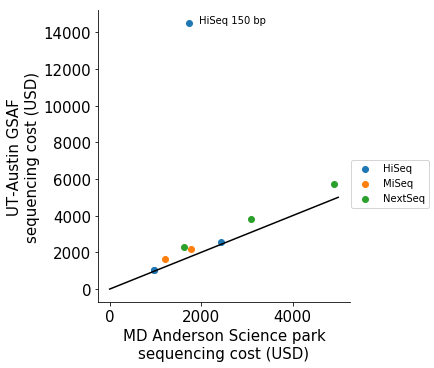
We can see that sequencing prices from both centers are proportion to each other, with NextSeq runs tend to be of higher cost per sequenced base.
I noticed there was a HiSeq run being an outlier in the plot (~14000 USD at UT-Austin GSAF vs ~2000 USD at MDA Smithville), it is possibly a mis-labeling of a full run (8 lanes for HiSeq) price instead of a per-lane-price. For the next analysis, I will assume that’s the case.
I am interested at the head-to-head comparisons between the two sequencing centers for different sequencing run types,
merge_df = gsaf_price_df\
.groupby(['Platform','machine','ends','total_base'], as_index=False)\
.agg({'gsaf_price':np.min})\
.merge(mda_price_df, how ='inner') \
.filter(regex = 'price|machine|ends|base')\
.pipe(pd.melt, id_vars = ['machine','ends','total_base'],
var_name = 'center',
value_name = 'price')\
.assign(center = lambda d: np.where(d['center'].str.contains('gsaf'),
'UT-Austin GSAF',
'MD Anderson Science park')) \
.assign(price = lambda d: np.where(d.price > 10000, d.price / 8, d.price))
p = sns.FacetGrid(data = merge_df,
col = 'machine',
sharex=False,
size = 5)
p.map(sns.barplot, 'total_base',
'price',
'center',
palette = okabeito_palette(),
hue_order = ['MD Anderson Science park',
'UT-Austin GSAF'])
p.add_legend(bbox_to_anchor=(0.5,0.8),
fontsize=12)
p.set(xlabel = '',
ylabel = '')
p.set_titles('{col_name}')
p.fig.text(0.4, 0, 'Sequencing cycle (nt)', fontsize = 15)
p.fig.text(0, 0.8, 'Per-lane-price (USD)', fontsize = 15, rotation=90)
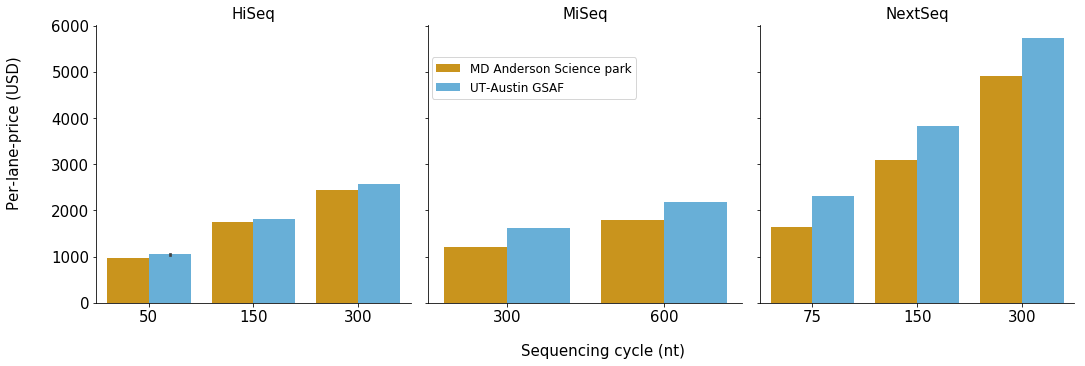
From the figure, it looks like UT Austin GSAF has a higher price for every sequencing type.
For the comparison in HiSeq runs, GSAF is running HiSeq 4000 while MD Anderson Science Park is running HiSeq 3000, so that maybe one of the reason. For the other ones, seems like the machines are the same.
